Automation as a fundamental building block for cloud–native transformation

As part of the synvert mission of creating high-performing organizations, we see automation as a critical building block.
Automation is all about adding technology that performs tasks with reduced human assistance. It offers numerous benefits to organizations, including increased speed, scalability, security, time-to-market, management efficiency, agnosticism, quality improvement, and system availability. All these advantages contribute to operational excellence, cost-effectiveness, competitiveness, and overall customer satisfaction.
In this article, our goal is to go one lever deeper going from theory to practice on what exactly we prioritize automating in a Cloud Native setup with our customers. In the second section of this article, we give you insights into how we did it with a real-world example for a customer that needed to avoid cloud vendor lock-in, leveraging open-source tools as much as possible.
What automation do we prioritize at synvert?
The prioritization regarding automating processes can vary depending on an organization’s specific needs, goals, and maturity. However, some common processes that advise teams to prioritize and help implement are:
1. Testing
Automating various types of testing, such as unit testing, integration testing, and acceptance testing, helps us speed up the testing process and improve the quality of releases. We see that over time, our lead time for change decreases to less than half the time and we’re able to deploy twice as much and more reliably compared to similar projects with no automated testing in place.

2. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Automating build, test, and deployment processes is a crucial component of a cloud-native setup, enabling organizations to deliver their products and services faster and more frequently.
At synvert, we rely on tools like GitHub Actions or Gitlab CI for our CI/CD requirements and prioritize agnostic practices to ensure scalability in the face of growth.
3. Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
We advocate for adopting Infrastructure as Code (IaC) practices to automate the provisioning and management of infrastructure, which can improve efficiency and reduce the risk of errors. IaC also enables better cost management by providing an overview of all resources used by applications and services. We emphasize the importance of describing all resources in our IaC to prevent the creation of unused resources and reduce unnecessary expenses.
4. Configuration as Code
Automation combined with configuration as code practices can bring significant benefits to organizations. By automating infrastructure and system configurations, it is possible to improve consistency, speed, and accuracy while reducing the risk of errors.
At synvert, we value the use of configuration as code and automation as a way to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Additionally, it enhances collaboration, security, and traceability, which are crucial factors in a cloud-native environment.
5. Monitoring and Logging
Automated monitoring and logging play a crucial role in enabling organizations to swiftly detect and troubleshoot issues, leading to improved availability and reliability of their applications and infrastructure. We take this a step further by setting up alerting and integrating multiple communication tools to ensure that we are immediately notified when any alert is triggered, allowing us to take prompt action and prevent any possible downtime or issues.
6. Data backup and recovery
Data backup and recovery is a critical part of any organization’s disaster recovery plan. In the event of a data loss, having a comprehensive backup system in place can mean the difference between quickly recovering from the loss and experiencing costly downtime. Automated data backup systems can help organizations ensure that critical data is backed up regularly, securely, and efficiently. Cloud-based backup solutions offer added protection by storing backups off-site, away from the organization’s primary infrastructure.
At synvert, we understand the importance of data backup and recovery and work with our clients to develop and implement robust backup and recovery strategies tailored to their specific needs. We prioritize security, redundancy, and ease of use to ensure that our clients can quickly recover from any data loss or system failure.
7. Security
Automating security processes can strengthen an organization’s security posture, mitigate the risk of security incidents, and expedite its response to security threats. It is imperative for organizations to prioritize security in their automation efforts and ensure that security is integrated into all facets of their operations to safeguard sensitive data from possible breaches.
At synvert, some common examples are the incorporation of tools that examine the code, container images, and IaC for any security breaches and aid us in maintaining the defined security posture on every project we undertake.

8. Reporting and analytics
Automating the report and analytics generation process can offer valuable real-time insights into critical performance metrics, empowering organizations to make informed, data-driven decisions. We prioritize ensuring that we have accurate and comprehensive reports with actionable data that can drive our projects and improve business outcomes. This information is not only useful for our development team but also for our business leaders to make strategic decisions.
Once again, automation offers numerous benefits to organizations, including increased efficiency, faster time-to-market, improved quality, enhanced security, better business management, and reduced risk of errors. By automating tasks and processes, organizations can streamline their operations, allowing for more informed decision-making and promoting business growth.
How we did it in a real-world cloud-native transformation
To explain better the importance of automated processes regarding cloud-native transformation we will use one of our customer’s journeys as an example. In this specific example, we had a very open-source approach, since the customer wanted to be cloud provider agnostic.
In this particular project, our team built a new cloud infrastructure from the ground up. We identified a few opportunities that could be automated to simplify the delivery process and streamline the work of the engineering teams. By automating these processes, we increased the Lead Time for Change and number of deployments drastically.
1. Automating the infrastructure layer with IaaC
We defined the entire infrastructure using Terraform. This allowed us to easily provision our infrastructure, from the network and Kubernetes cluster to the load balancer and beyond, creating an immutable infrastructure that was easy to manage. Using this tool, we saved time and effort while ensuring the reliability and consistency of our infrastructure. To learn more about the benefits of immutable and ephemeral infrastructure, please refer to our article on the subject.
2. Automating the application runtime layer with Kubernetes
Once our infrastructure was operational, our focus shifted to deploying and serving the customers applications. To manage our Kubernetes applications, we utilized Helm charts, a package manager that allowed us to configure all the applications with the necessary templates for efficient deployment.
3. Automating the Release Pipeline
In terms of CI/CD, we have implemented specific actions to initiate certain procedures. Upon the developer’s submission of a pull request (PR) for merging with the primary branch, a series of tasks are activated. These tasks include running unit tests, conducting security, code quality, vulnerability checks, and more.
This ensures that any merged code will not cause any disruptions, maintain its quality, and comply with team standards. After successfully passing all procedures, the pull request is deemed ready for merging. Once the developer completes the merge, the continuous deployment process is triggered. This process starts with the generation of a container image, usually done through Docker, followed by the publication of the image to a container registry. The deployment process then starts, leveraging the pre-existing Helm charts configuration.
4. Automating observability
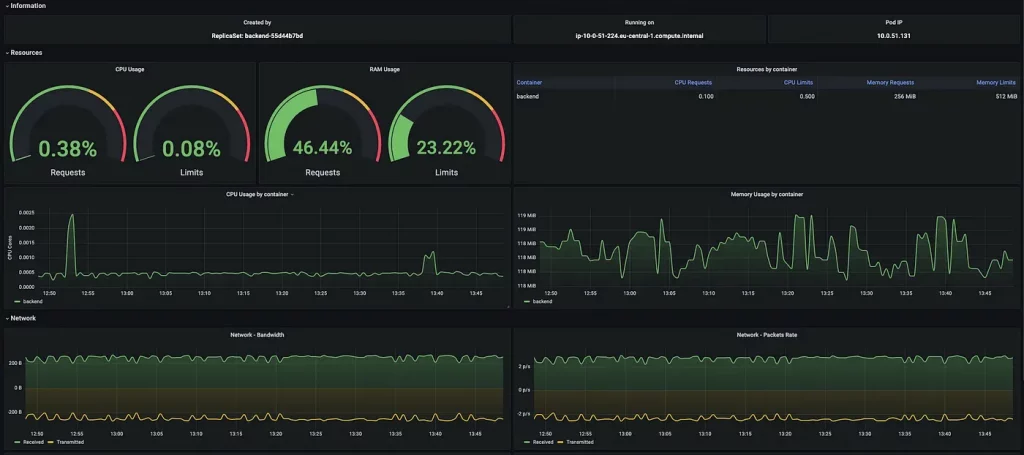
In terms of monitoring, we used Prometheus, a widely-used open-source monitoring system that features a flexible query language, an efficient time series database, and a modern alerting approach. Prometheus collects our application metrics, providing us with valuable insights into factors such as latency and downtime, and even scales automatically. For more information on best practices related to this topic, we recommend reading our article.
In this specific system, there were two additional tools, namely Grafana and Loki, which are part of the same ecosystem as Prometheus. By utilizing Prometheus as a data source, Grafana retrieves metrics from it, allowing us to design dashboards that track various aspects of our applications, such as resource usage, latency, network bandwidth, and more.
Loki is employed as a source of data, collecting logs from the applications, which can then be accessed through Grafana.
Final thoughts
At synvert, our approach to Cloud Native Transformation involves delving into the foundational building blocks that underpin it. This uniquely positions us to guide customers to think beyond the tools and focus on the purpose behind their endeavors.
In the scenario presented, while leveraging managed services from a public cloud provider is often advantageous, we assisted the customer in maintaining agnosticism while still achieving their ultimate goals. By prioritizing the needs of their end users and fostering a seamless developer experience, we facilitated continuous product development with a strong emphasis on quality and speed!













